Spectroscopy Measurement Methods and Techniques | |
The Spectroscopy group is all about probing the electronic and local atomic environment of atoms in materials using X-ray absorption and the relaxation process resulting in X-ray fluorescence. To do this, we utilize three distinct methods described below.
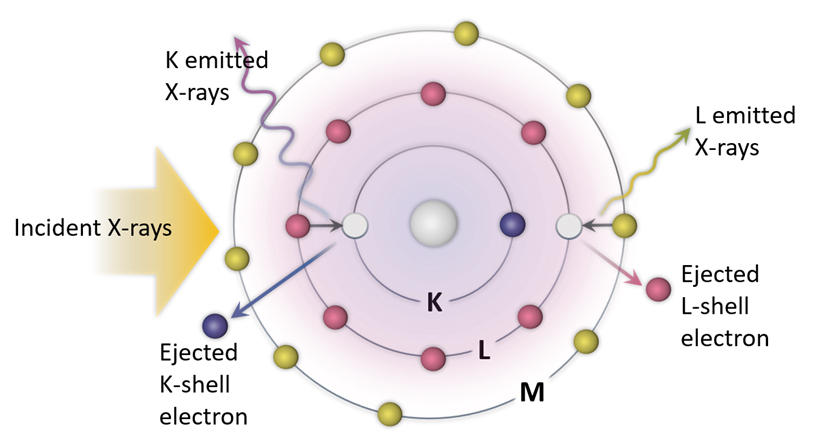
The first is to scan the X-ray energy through the absorption edge, exciting a core electron such as the 1s electron in the k-shell shown at right, and recording the total absorption by the sample. This process is also proportional to the resulting fluorescence caused by filling the core hole, or the partial fluorescence for high energy resolution fluorescence detection (HERFD). Click here for more info on HERFD.
Another measurement technique involves setting the X-ray energy high above the absorption edge, and recording the fluorescent X-rays resulting in X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES). Click here for more info on XES.
The third technique is to scan the X-ray energy far above the absorption edge and record the energy loss from interaction of the core electrons with X-rays (X-ray raman scattering). Click here for more info on X-ray raman scattering.
|  |

